Why do certain
substances taste sweet, sour, bitter, or salty? Of course, it has to do with
the taste buds on our tongues. But how do these taste buds work? For example,
why does sugar taste sweet to us? The answer to this question remains elusive,
but it does seem clear that sweet taste depends on how certain molecules fit
the “sweet receptors” in our taste buds.
One of the mysteries of
the sweet taste sensation is the wide variety of molecules that tastes sweet. The
chemical structure of common table sugar (called sucrose) is shown on the
right.
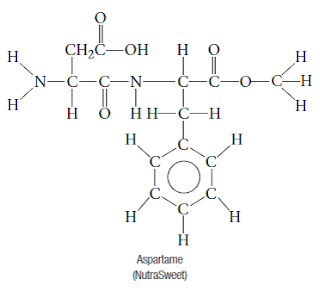
One artificial
sweetener, aspartame, is used in many products including candy and diet soda.
Some people are allergic to aspartame.
Another widely used
artificial sweetener is sucralose which is made by modifying sucrose (compare
the structure of sucralose to sucrose shown above). Look at the groups with
blue circles in each structure. Sucralose is 600 times as sweet as sucrose and
is used to sweeten beverages, baked goods, yogurt, and desserts.
DOWNLOAD FULLTEXT : CLICK HERE





No comments:
Post a Comment